Atlassian MCP Server: Installation Best Practices & Use Cases
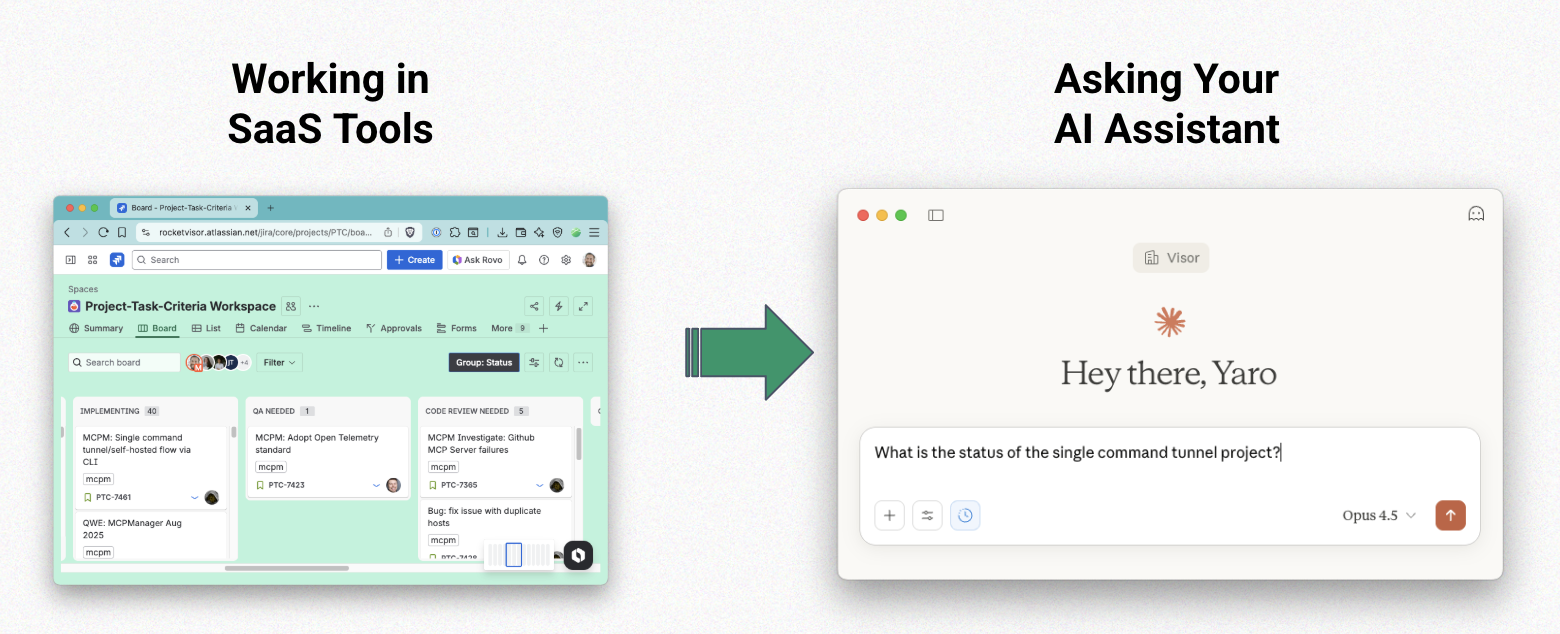
The way we work is fundamentally changing. Instead of jumping between Jira, Confluence, and a dozen other SaaS tools to piece together information, teams are increasingly asking their AI assistant to streamline workflows and improve efficiency.
Whether checking the status of a sprint, updating a Jira ticket with context from a customer call that you store in another app entirely, AI can do all of that when properly connected to external tools.
This is where the Model Context Protocol (MCP) comes in. And Atlassian is leading the charge in making enterprise AI assistants actually useful by launching the Atlassian MCP server that connects to clients like Claude and Cursor, allowing AI systems to directly work with your Jira and Confluence data.
Atlassian’s Continued Investment in MCP
Atlassian isn’t just experimenting with AI; they’re all in. Their investment in AI extends beyond launching a second MCP server (Rovo). They also keep improving the servers they put out there.
In the May 2025, they launched the Atlassian’s remote MCP server, improving upon it in the months to follow (which we’ll get to below). Clearly, they’re committed to making AI work for their customers.
In February 2026, they launched Rovo MCP, which features OAuth 2.1 authorization, the most secure auth flow for MCP servers. Again, they demonstrated their commitment to making the Atlassian ecosystem of tools and data compatible with the AI tools their customers also use.
Remote MCP Servers
Both Atlassian and Rovo servers are remote MCP servers. There are three different types of MCP servers. While remote MCP servers are the easiest to implement, they are hardest for publishers of MCP servers to maintain.
Remote servers are the most popular type of MCP server deployment for large SaaS brands because they recognize that customers need easy-to-implement servers that can install easily into clients like Claude and Cursor.

The SSE to HTTP Migration: Why It Matters
In late 2025, Atlassian made a significant architectural change to their Atlassian MCP server, migrating from Server-Sent Events (SSE) to HTTP. While this might seem like a technical detail, it has major implications for enterprise adoption:
Why HTTP is better for enterprise environments:
- Firewall-friendly: HTTP requests work seamlessly through corporate proxies and firewalls, while SSE connections often get blocked or timeout
- Better observability: Standard HTTP requests are easier to monitor, log, and debug using existing enterprise tooling
- Reliability: No long-lived connection issues—each request is independent and can be retried
- Gateway compatibility: Works naturally with API gateways, load balancers, and enterprise security infrastructure
This shift signals that Atlassian is thinking seriously about how MCP needs to work in real-world enterprise environments with security teams, compliance requirements, and existing infrastructure.
What the Atlassian MCP Server Actually Connects To
The Atlassian MCP server currently provides AI access to:
- Jira: Read and update issues, projects, boards, and workflows
- Confluence: Access pages, spaces, and documentation
- Compass: Connect to your component catalog and architecture data
Notably absent? Bitbucket. While this may come in the future, it means teams using Atlassian for their entire DevOps pipeline will need to supplement with other MCP servers (like GitHub’s) if they want AI to interact with their code repositories.
Similarly, they have a separate server for Rovo. Notably, these servers are different than APIs. It’s a common myth that MCP is simply an API. We cover why that is below.
Real-World Use Cases: Why the Atlassian MCP Server Matters
MCP represents a generational shift in how we work. Instead of asking “Where is that information?” teams can now ask their AI assistant to synthesize and act on information across their entire tool stack.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Sprint Planning: “What’s the status of the single command tunnel project?” Your AI pulls current Jira board state, related Confluence documentation, and can even create new tickets based on the conversation.
- Incident Response: “Summarize all P1 incidents from last week and draft a postmortem outline.” Your AI gathers Jira incidents, pulls relevant Confluence runbooks, and structures the information for you.
- Project Handoffs: “Get me up to speed on the MCPManager August 2025 project.” Your AI reads through Jira epics, associated Confluence project pages, and gives you a comprehensive briefing.
- Cross-team Collaboration: “What feedback did the design team have on the authentication flow?” Your AI can pull from Confluence comments, Jira tickets, and synthesize the discussion.
The key insight: AI becomes exponentially more useful when it has context from multiple systems, not just one.
The Multi-Server Reality (And Why It Complicates Things)
Here’s where things get interesting (and complex). While the Atlassian MCP server is powerful, most teams don’t work exclusively in Atlassian tools. A typical engineering team might need:
- Atlassian MCP for Jira and Confluence
- GitHub MCP for code repositories and pull requests
- Notion MCP for company wiki and documentation
- Slack MCP for team communications
- Linear MCP for product planning (if they’re not using Jira for everything)
Each additional MCP server connection creates:
- Authentication sprawl: Managing credentials and tokens across multiple services
- Inconsistent security policies: Different servers have different access controls
- No unified audit trail: Who accessed what data from where?
- Expanded attack surface: Each connection is a potential vulnerability
- Token cost bloat: AI sifting through unnecessary tools increases API costs
This is why MCP governance and observability become critical as you scale beyond a single MCP server. In the section and video below, we go into the best way to set up multiple MCP servers securely.
Atlassian MCP Server Installation Best Practices
Let me show you how to install and configure the Atlassian MCP server properly, with the governance and security controls that enterprise teams actually need.
Step 1: Use a Gateway Architecture
Rather than connecting Claude Desktop directly to individual MCP servers, use an MCP Gateway that sits between your AI assistant and your MCP servers. This architecture provides:
Centralized governance: Set security policies once, apply them across all servers PII detection: Automatically flag sensitive data before it reaches your AI Runtime guardrails: Enforce what actions AI can and cannot take Unified audit logs: See all AI-to-data interactions in one place RBAC (Role-Based Access Control): Different team members get different access levels
In the video above, I’m using MCP Manager by Usercentrics to create this gateway, but the principles apply regardless of your gateway solution.
Step 2: Configure the Atlassian MCP Server in Your Gateway
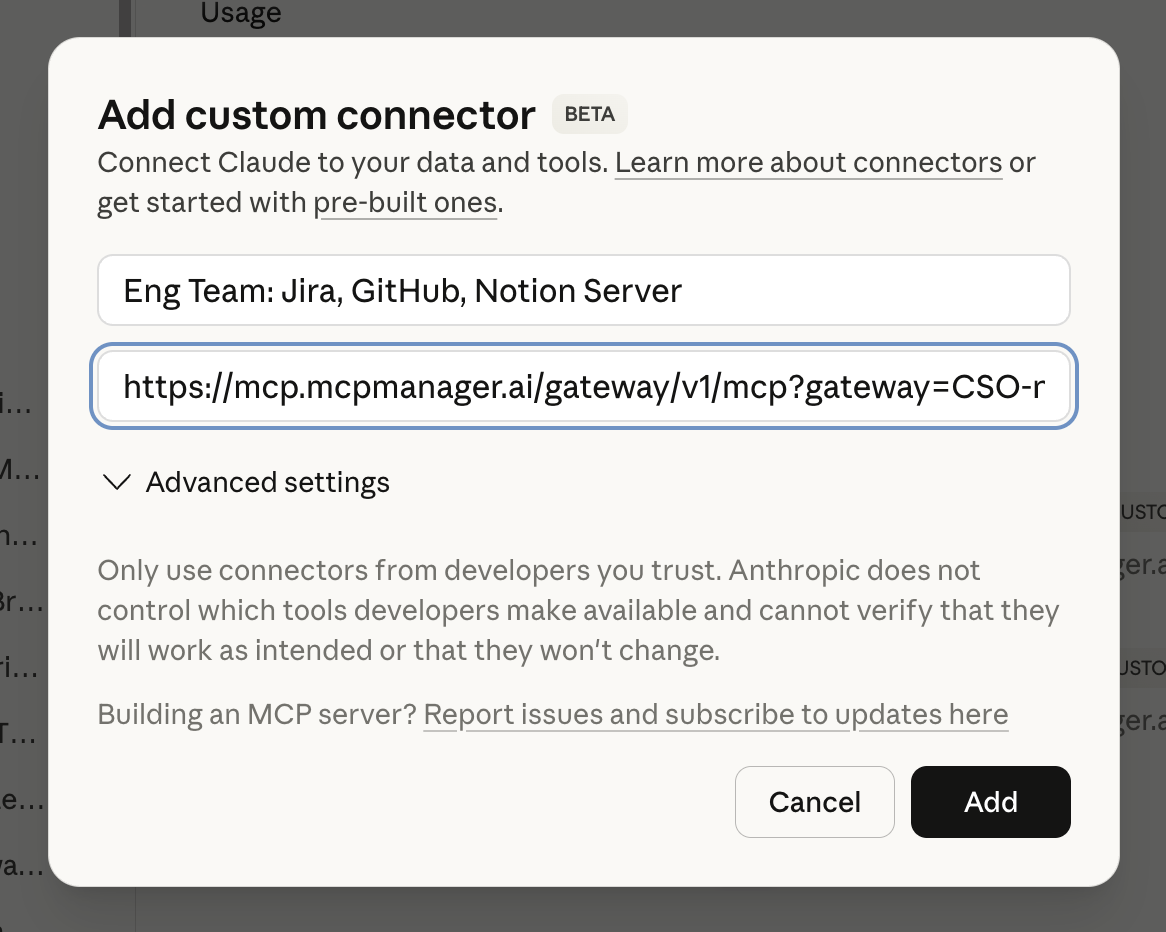
Instead of adding the Atlassian MCP server URL directly to Claude Desktop, add it to your MCP Gateway configuration:
- Copy the Atlassian remote MCP server URL from the Atlassian documentation
- Paste it into your gateway configuration (in the video, this is done through the MCP Manager UI)
- Add any additional MCP servers your team needs (GitHub, Notion, etc.)
Why this matters: Your gateway now acts as a single point of control. You’re not managing 5 different MCP server connections—you’re managing one gateway that routes to multiple servers.
Not sure what an MCP gateway is? Check out this overview video. 👇
Step 3: Implement Tool-Level Provisioning
Here’s a critical best practice many teams miss: not all AI interactions need access to all tools.
The Atlassian MCP server exposes dozens of tools (functions) like:
- jira_get_issue
- jira_create_issue
- jira_update_issue
- jira_delete_issue
- confluence_get_page
- confluence_create_page
In your gateway, you can selectively enable only the tools you want AI to access. For example:
- Read-only access: Enable jira_get_issue but disable jira_create_issue and jira_delete_issue
- Specific workflows: Only allow ticket creation in certain Jira projects
- Cost optimization: Fewer enabled tools = faster AI responses and lower token costs
By limiting the tool surface area, you:
- Reduce the risk of accidental data modifications
- Improve AI response quality (less noise to sift through)
- Lower your token costs
- Make debugging easier
Step 4: Configure Identity Management
When AI accesses your Jira MCP server data, who is it acting as? This matters for:
- Audit logs: Compliance teams need to know which human triggered which AI action
- Access control: AI should respect the same permissions as the human using it
- Accountability: If something goes wrong, you need to trace it back
Your MCP Gateway should handle identity passthrough, so when you ask Claude (or whatever client you use) to access Jira, it’s using your credentials and permissions, not a shared service account.
MCP Manager handles identity management, forcing users to authorize the server with their Atlassian credentials. This makes MCP observability possible and makes deploying at scale easier for IT.
Step 5: Connect MCP Client to Your Gateway
Once your gateway is configured with the Atlassian MCP server (and any others), you simply:
- Copy the gateway URL from your MCP Gateway dashboard
- Paste it into Claude Desktop’s MCP configuration
- Authenticate
That’s it. Claude is now connected to all the MCP servers in your gateway through a single, governed connection.
(BONUS) Step 6: Access Audit Logs and Usage Dashboards
Because you set up your MCP servers using an MCP gateway in MCP Manager, you can get audit logs and dashboards of overall server and token usage. In addition, you get monitoring and alerts.
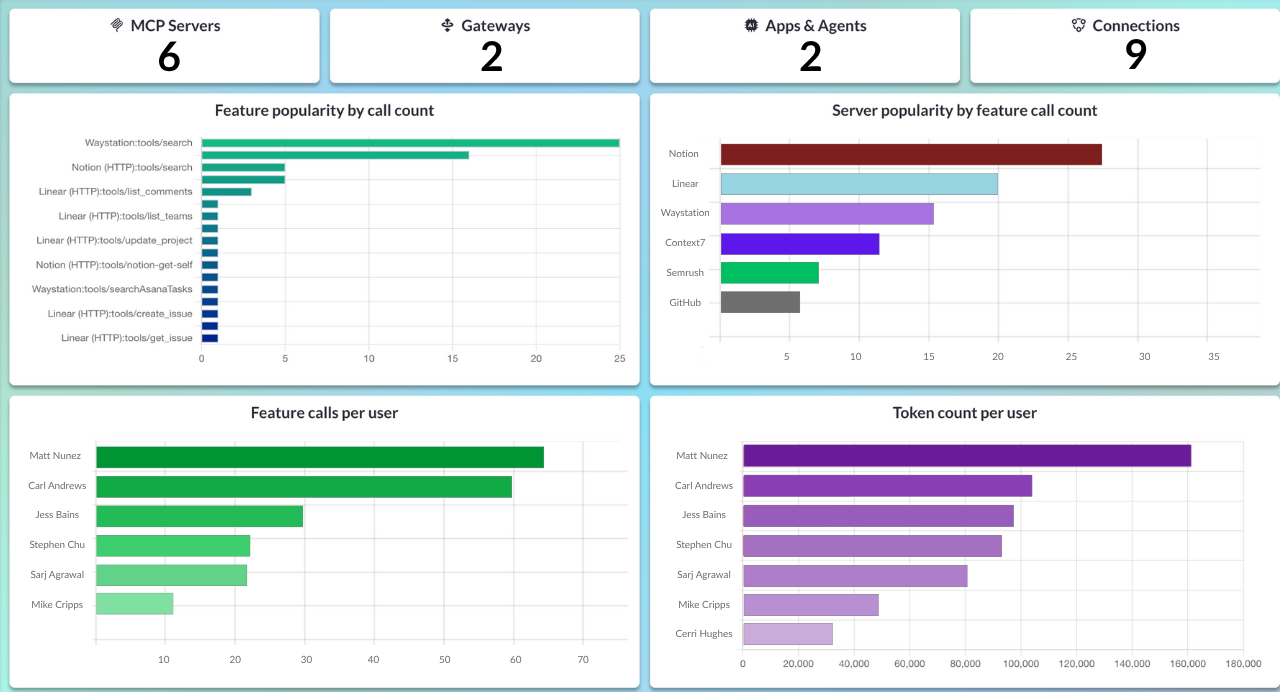
Using the Atlassian MCP Server in Practice
With everything set up, you can now ask your MCP client (in this case, Claude) questions like:
“What is the status of the single command tunnel project?”
Claude will:
- Use the Jira MCP server to query your board
- Pull relevant ticket details
- Synthesize the current state
And in your MCP Gateway dashboard, you’ll see:
- Audit log entry: “User Yaro queried Jira project PTC at 2:34 PM”
- Tools called: jira_search_issues, jira_get_issue
- Data accessed: Project keys, issue summaries
- Response time: 1.2 seconds
This visibility is what makes MCP production-ready for enterprise teams.
Why Governance Matters for Jira MCP Server Adoption
Let’s be honest: most developers want to jump straight to “Claude, update this Jira ticket” without thinking about governance. But here’s why that’s shortsighted:
Compliance requirements: If you’re in healthcare, finance, or any regulated industry, you need audit trails showing who accessed what patient/customer data through AI. In the video below, we show you how to get audit logs that fulfill these compliance requests.
Security incidents: When (not if) something goes wrong, you need to know exactly what happened. That’s where audit logs come in. You also want to make sure that you are preventing common threats like MCP rug pull attacks, along with prompt injection attacks and tool poisoning. MCP Manager’s gateway helps you do just that.
Cost management: Uncontrolled MCP usage can rack up API costs quickly. Because our MCP gateway lets you provision tools, you can stop context bloat from occurring (which is what happens when servers provide AI with more tools to sift through than they need.) In addition, the usage dashboards we discussed earlier also let you see where the main usage (and, therefore, costs) are happening. This helps you decide whether the ROI on those token costs are worth it.
Data leakage prevention: PII in Jira tickets can accidentally get sent to Claude’s API without detection
In addition, MCP Manager’s MCP Gateway provides:
- Dashboards showing usage patterns across teams
- Alerts when unusual activity is detected (e.g., mass ticket updates)
- Guardrails preventing certain actions (like bulk deletion)
- PII detection flagging sensitive data before it leaves your infrastructure
Getting Started with the Atlassian MCP Server
The Atlassian MCP server is one of the most mature and well-supported MCP implementations available today. Atlassian’s continued investment—from the SSE to HTTP migration to the Rovo MCP launch—shows they’re serious about making AI a core part of how teams work.
But as you scale beyond simple read-only queries to actual AI-driven workflows, you need governance, observability, and security controls that MCP itself doesn’t provide.
That’s where an MCP Gateway architecture comes in.
Want to see this in action? The video above walks through the complete setup process, showing how to securely connect the Atlassian MCP server (along with GitHub and Notion) to Claude through an MCP Gateway that provides the governance and visibility enterprise teams need.
You can try MCP Manager with a free 2-week trial by scheduling an onboarding call, where we’ll help you set up the Atlassian MCP server and any other servers your team needs—with all the security and governance controls built in from day one.